Tourism-Induced Land Use Transformations, Urbanisation, and Habitat Degradation in the Phu Quoc Special Economic Zone
Nguyen, C. T.+, Downes, N. K., Sitthi, A., & Losiri, C., 2025. Tourism-Induced Land Use Transformations, Urbanisation, and Habitat Degradation in the Phu Quoc Special Economic Zone. Urban Science, 9(1), 11. 10.3390/urbansci9010011
Dynamic development of tourism activities and rapid urbanisation in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) can lead to significant land use and land cover changes (LULCCs) and environmental degradation, particularly in ecologically sensitive areas. This study examines the transformation of land use and its associated impacts on habitat quality and thermal environment in Phu Quoc Island (Vietnam) over a 20-year period (2003–2023). Using multi-temporal Landsat satellite imagery and random forest classification, we quantify LULCCs and assess the environmental consequences of urban expansion on habitat degradation and intensification of the island’s thermal environment, focusing on land surface temperature (LST) changes. Our analysis reveals that rapid urbanisation, driven by large-scale tourism and infrastructure developments, has led to a significant loss of forest and farmland, leading to a 5.6% decline in habitat quality and a marked increase in LST. The study also highlights the uneven distribution of urban growth, with the majority of expansion occurring in the southern and central regions of the island. By applying the InVEST Habitat Quality Model, we identify key zones of habitat degradation and offer insights into the spatial patterns of environmental sensitivity and changes. Our findings underscore the need for integrated land use planning and sustainable development strategies to mitigate the negative environmental impacts of SEZ-driven urbanisation on island ecosystems. This research provides critical guidance for policymakers, planners, and environmental managers to balance economic growth with environmental conservation in fragile island environments.
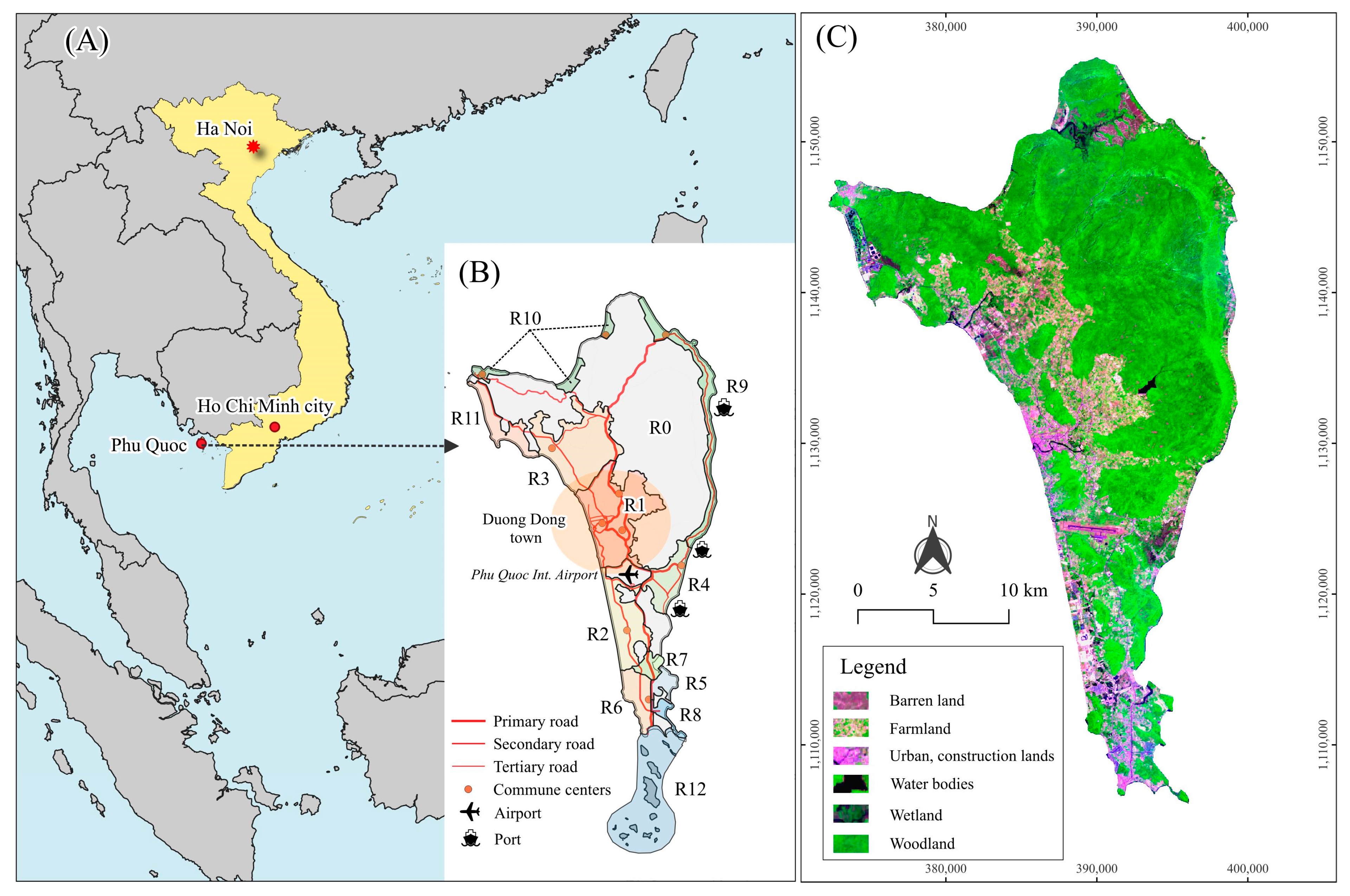
Maps illustrating the characteristics of Phu Quoc Island. (A) Phu Quoc is located in southwest Vietnam within the Gulf of Thailand. (B) Zoning development map of Phu Quoc defining twelve subdivision zones and highlighting the main urban centre of Duong Dong town and key supporting infrastructures. (C) Cloud-free composite image from Landsat 9 in 2023 of the entire Phu Quoc mainland (false colour composite: SWIR/NIR/Blue)
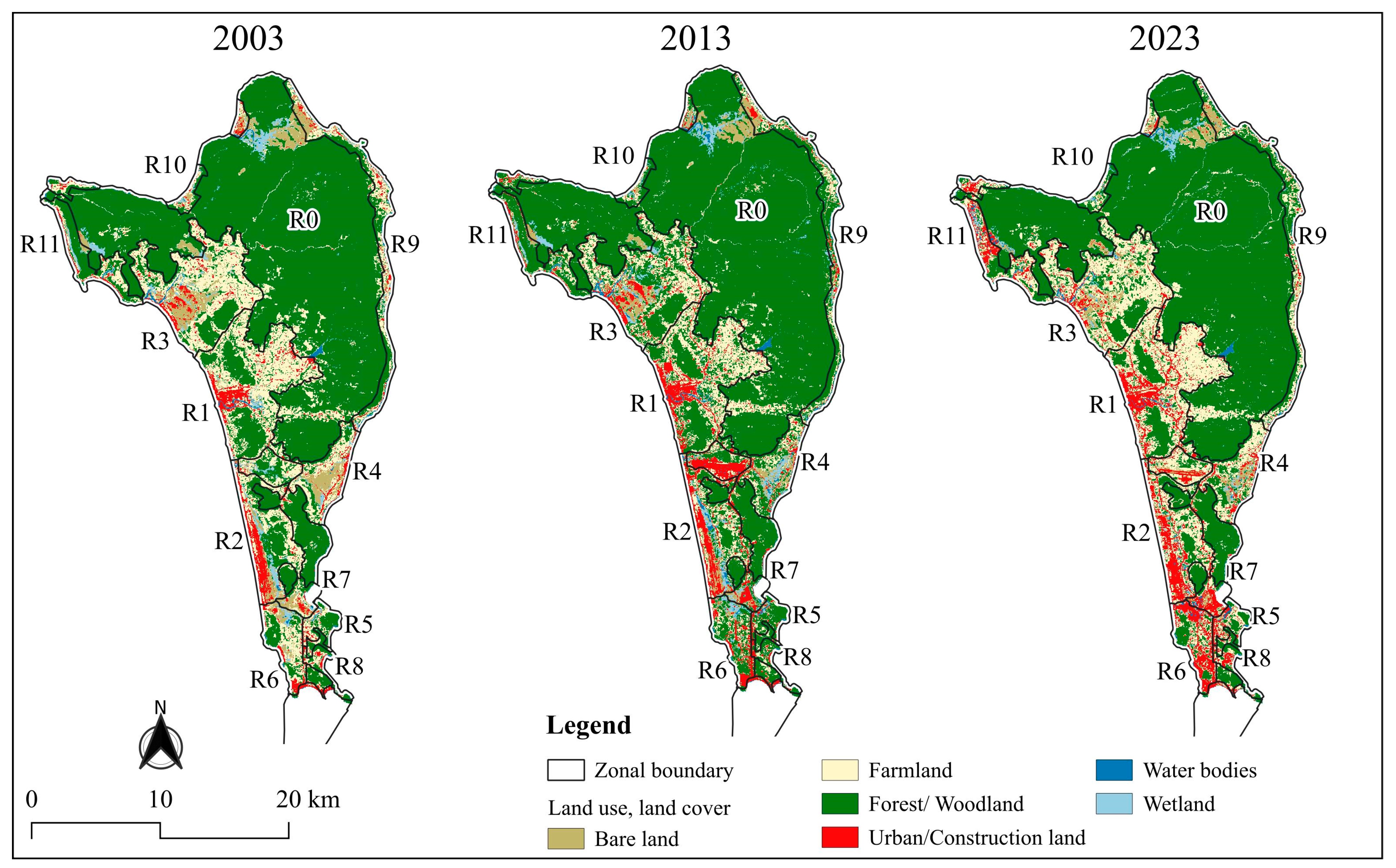
Spatial distribution of LULC categories in Phu Quoc from 2003 to 2023
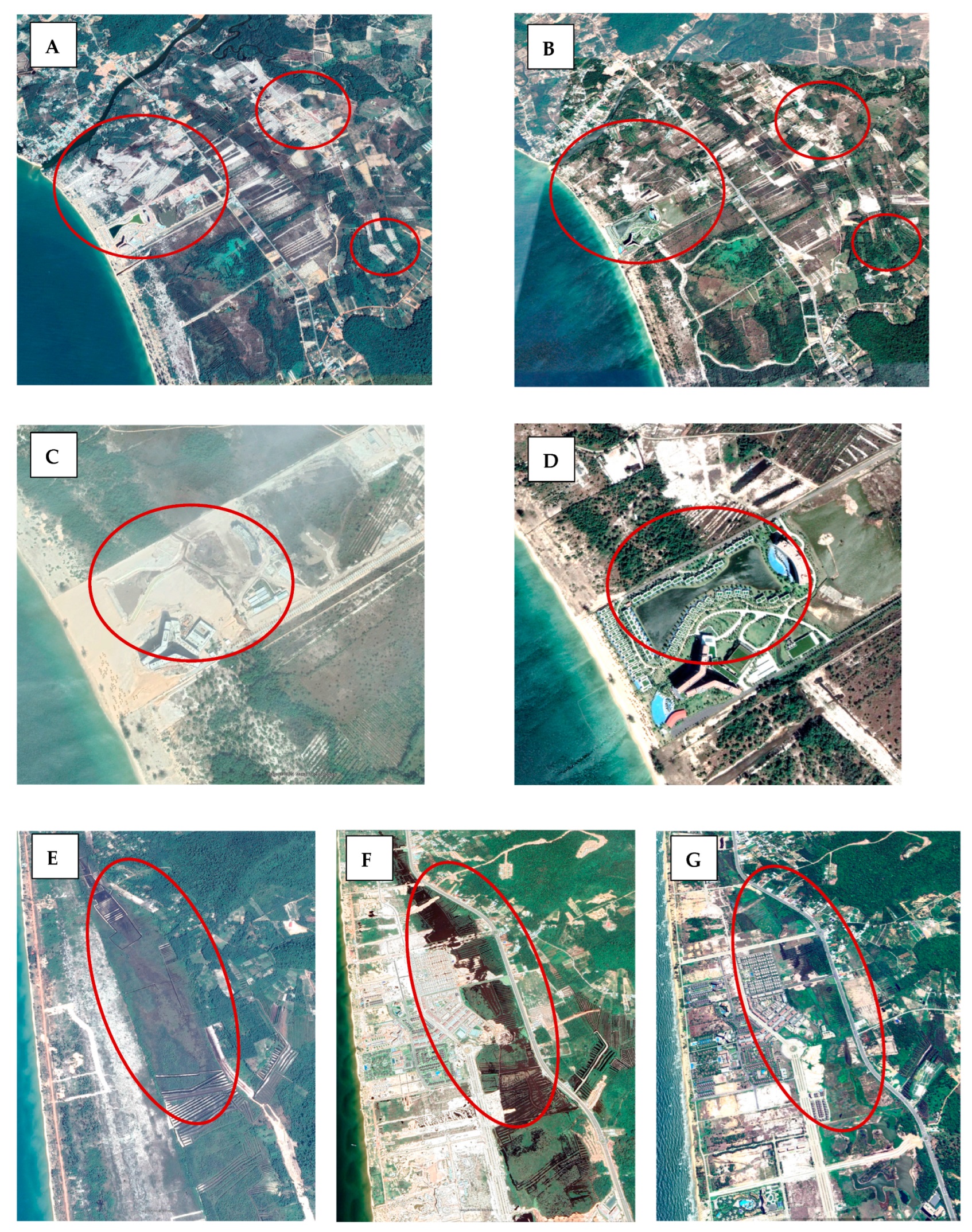

Examples from Google Earth: high-resolution images highlight the dynamics of LULCC and interconversion between LULC categories—(A–D) urban development and regreening on barren/construction lands and (E–G) wetland changes on Phu Quoc Island during the study period
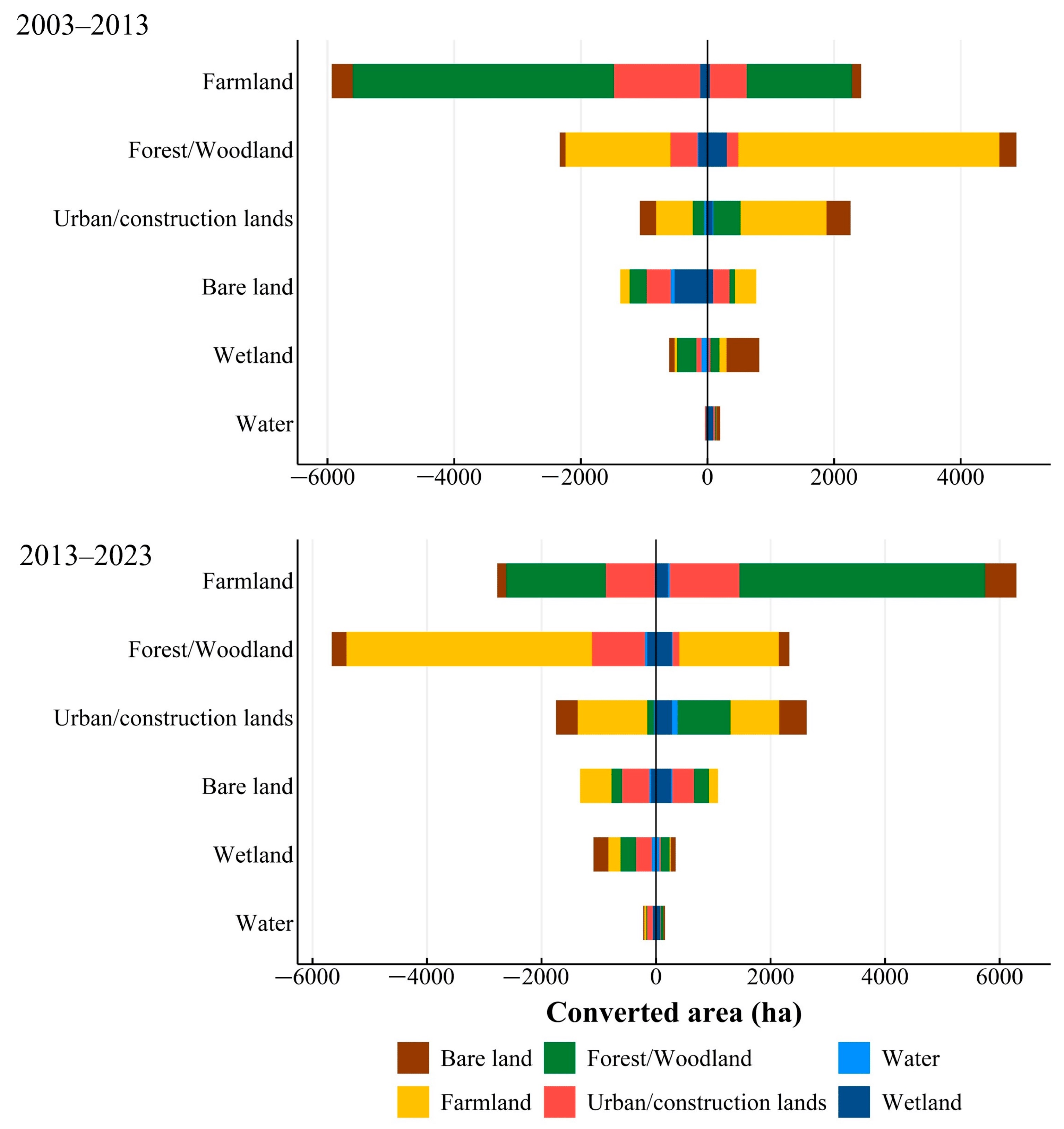
Converted areas between LULC categories for the periods 2003–2013 and 2013–2023. Vertical LULC categories are current LULC at the end of the period. Negative converted area and positive converted area are LUCC loss and gain, respectively.
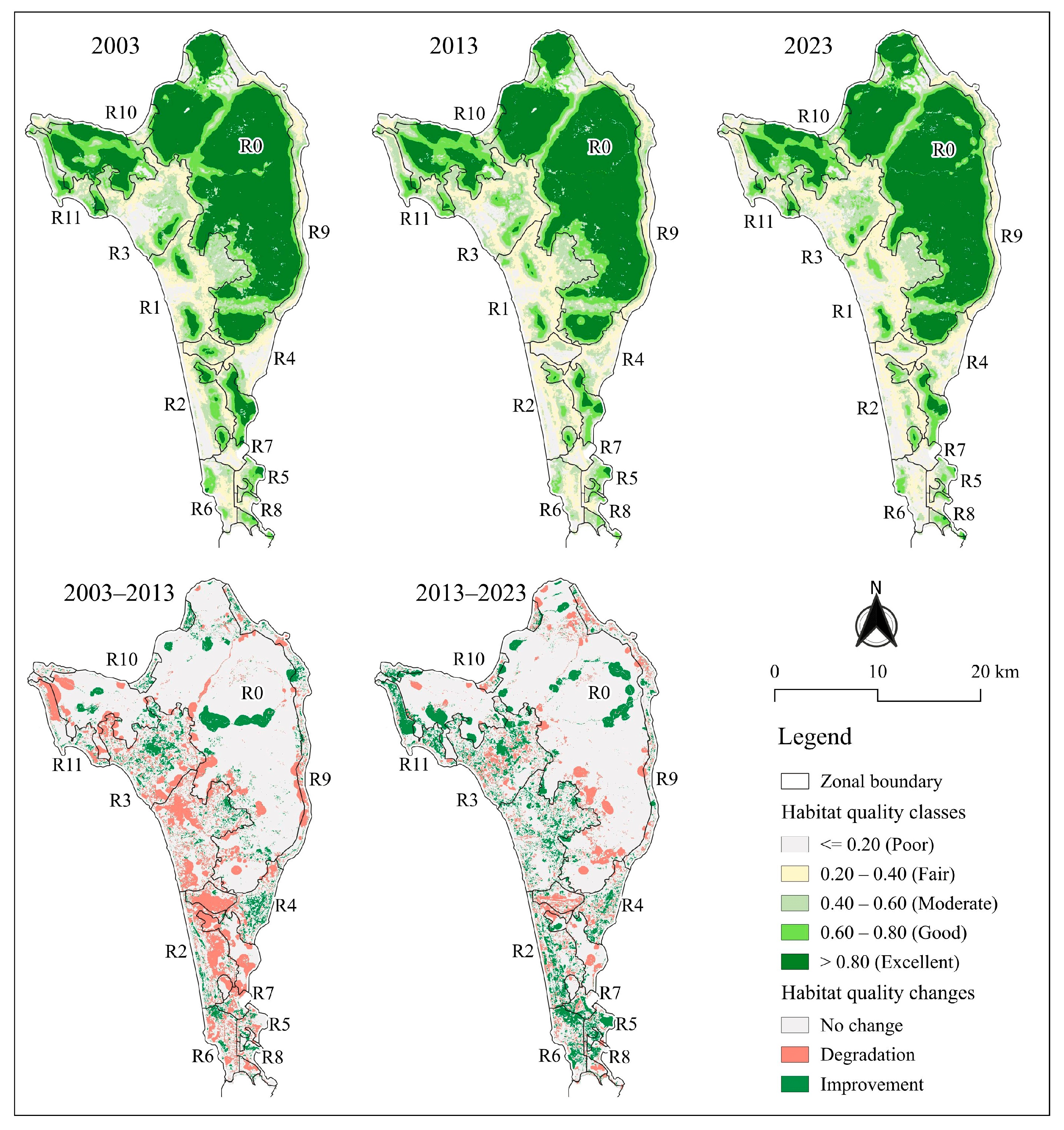
Simulated habitat quality in Phu Quoc in each year (top panel) and habitat quality changes over each ten-year period (bottom panel)
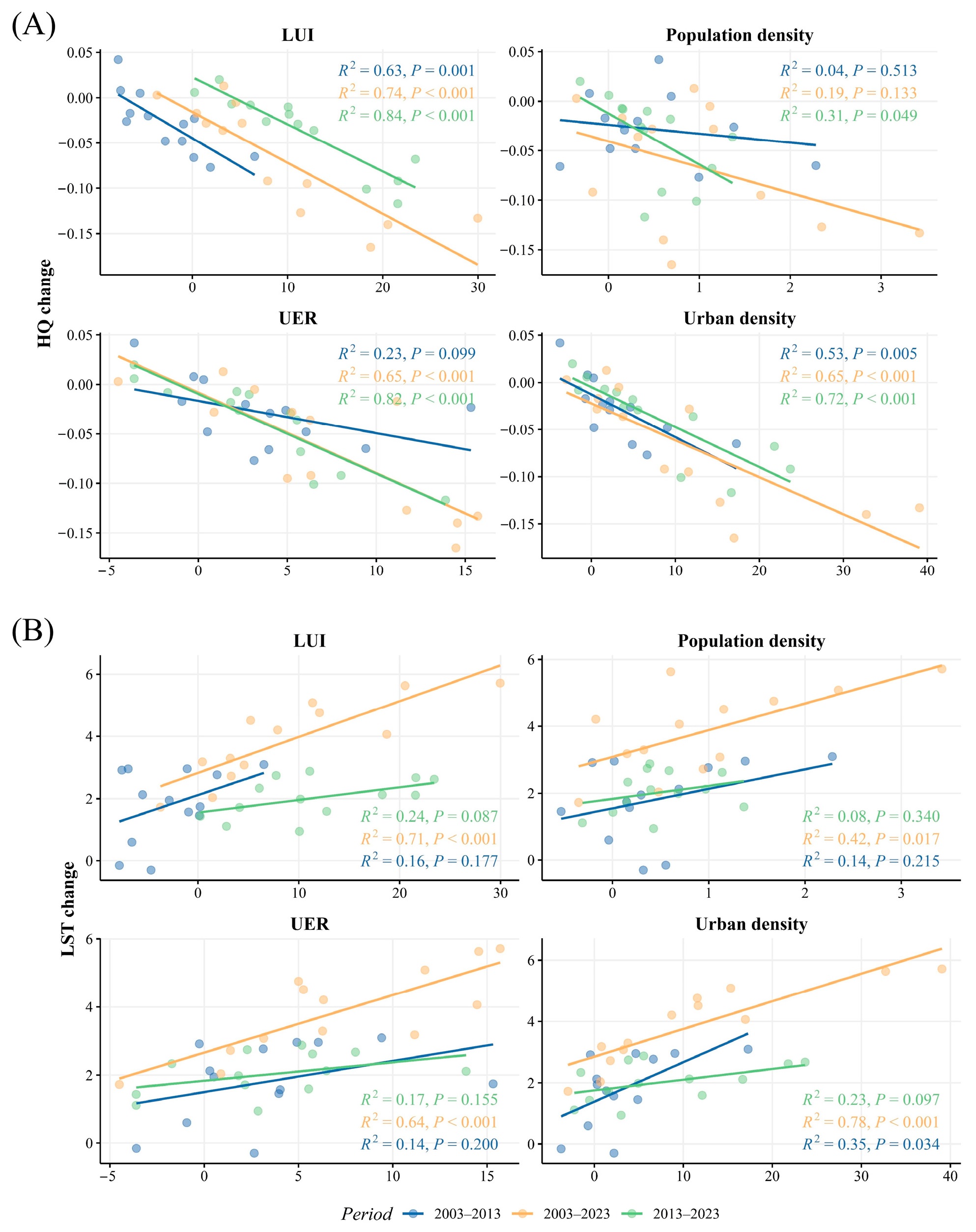
Relationships between (A) habitat quality and (B) thermal environment changes (LST, °C) and potential controlling factors. Vertical axes are HQ changes and LST changes, and horizontal axes are values of corresponding variables.